Debugging in HALO
Introduction
You’ve built an AI agent in HALO, and everything seems to be running smoothly—until you come across a conversation where the agent provides an incorrect or unsatisfactory response. What now? Debugging an AI agent might seem overwhelming at first, but with the right approach and the tools available in HALO, you can quickly identify the issue and improve your agent. In this article, we’ll share a structured step-by-step guide and practical examples to help you get started.
It’s important to remember that an AI agent cannot handle 100% of conversations perfectly. AI is probabilistic by nature, meaning it works based on probabilities rather than certainties. While it’s natural to want perfection, focusing too much on rare edge cases can detract from optimizing your agent for the majority of interactions. Instead, aim to refine your agent to handle the most common scenarios effectively, knowing that occasional exceptions are a natural part of working with AI.
Step 1: Analyze the Conversation
The first step in debugging is to thoroughly analyze the conversation where the issue occurred. Navigate to the Conversations section in HALO and locate the specific conversation. Then, click on the purple speech bubble where HALO responded. This will give you a detailed breakdown of what HALO did and why, including which agent handovers, tools, knowledge sources, or feedback were used to generate the response.
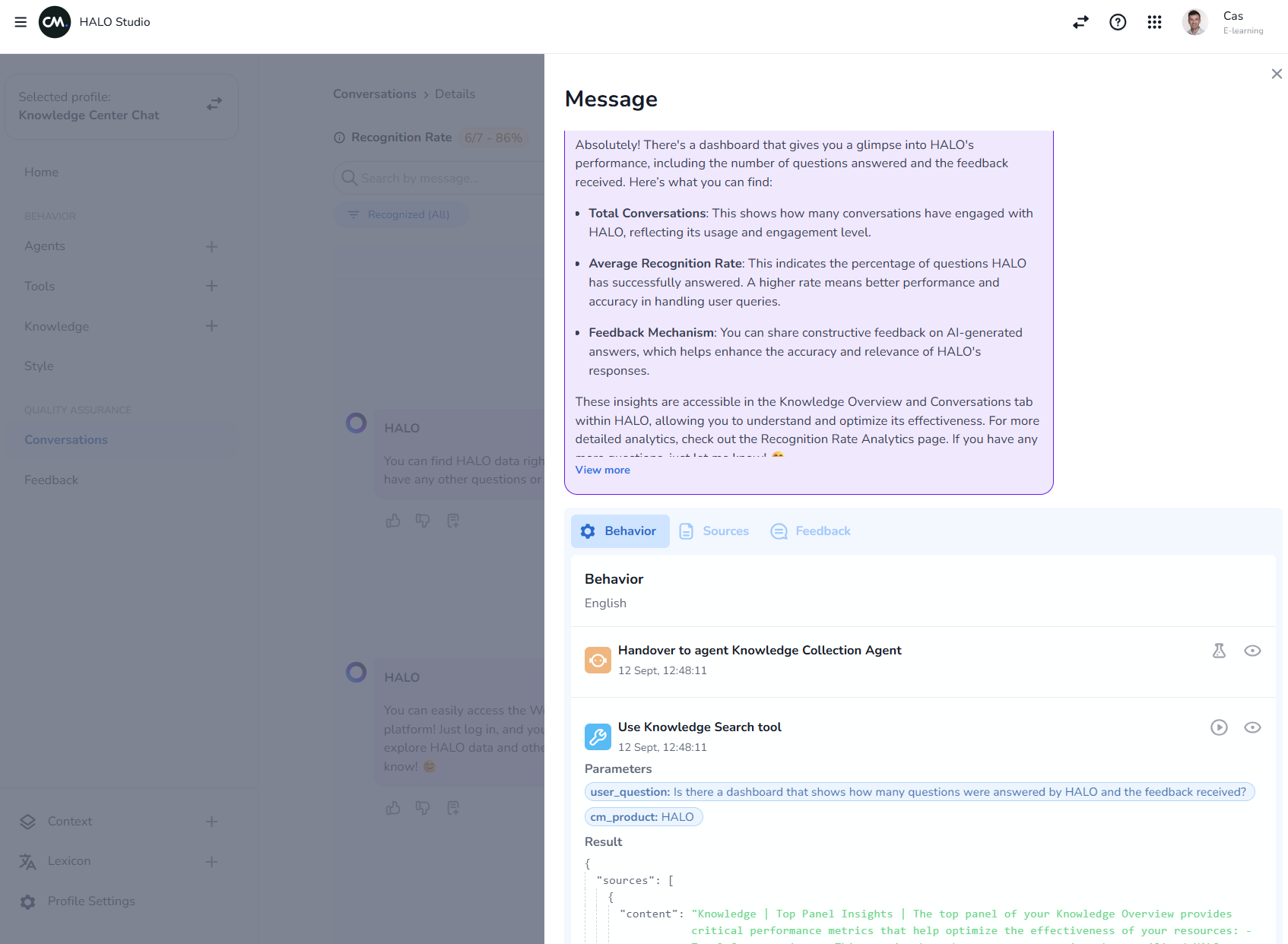
When analyzing the conversation, focus on three key aspects:
The user’s question: Was the question clear or ambiguous?
The agent’s response: Was the response incorrect, incomplete, or irrelevant?
The Behavior, Sources, and Feedback tabs: These tabs provide insights into which agent handovers, tools, knowledge sources, or feedback were used to generate the response.
By reviewing these details, you’ll gain a clear understanding of where the issue lies and what might need adjustment. To see this process in action, watch the video below, where we walk you through how to debug a conversation step by step.
https://vimeo.com/939498307/593438b902
Step 2: Identify the Source of the Problem
An AI agent in HALO generates its responses based on several components, such as tools, knowledge, and feedback. To pinpoint the source of the problem, follow these steps:
Check the routing: Verify if the question was routed to the correct agent. For example, if a user asks to speak to a representative, the conversation should be routed from the Routing Agent to the Handover MSC Agent. If this doesn’t happen, review the prompt of the Routing Agent and adjust it as needed.
Inspect the Behavior tab: Look at the steps the agent followed to generate the response. Confirm that the correct tools or knowledge sources were used.
Review the prompts: Ensure the agent’s prompts are clear and specific enough to trigger the correct actions.
Test the tools: Open the tool in the Tools section and test it with various input parameters to ensure it is producing the correct output. Tools are deterministic, meaning their behavior is predictable, so any issues here should be straightforward to identify.
Evaluate feedback: Check if feedback has overridden the agent’s output. If feedback caused an incorrect response, you can adjust or delete it via the Feedback Tab.
By systematically working through these components, you can identify the root cause of the issue.
Step 3: Improve the Agent
Once you’ve identified the source of the problem, it’s time to make improvements. Common issues typically fall into one of following categories: incorrect routing or handovers, ambiguous user input, tool errors, knowledge gaps, or mismatched tone of voice. Here’s how to address each:
Incorrect routing or handovers: If the conversation wasn’t routed to the correct agent, review the prompts and logic of the Root Agent or any other agent responsible for handovers. For example, if a user asks to speak to a representative but the conversation doesn’t reach the Handover MSC Agent, adjust the Agent’s prompt to ensure it correctly identifies and routes such requests. Additionally, verify that the handover logic is properly configured to handle edge cases or fallback scenarios.
Ambiguous user input: If the agent’s prompts are unclear or too generic, refine them to ensure they trigger the correct actions. For example, you can add more specific instructions or validation steps to guide the agent’s behavior. This is especially useful for improving how the agent handles ambiguous user input.
Tool errors: If the tool returned an error or incorrect output, open it in the Tools section and review its configuration. Test the tool with different input parameters to identify the issue, and adjust the settings or add additional steps to make it more robust.
Knowledge gaps: If the agent provided an incorrect response because the required information wasn’t available, add the missing knowledge via the Knowledge section. Upload a file or add a web crawler to gather relevant information, and synchronize the knowledge source to ensure the agent has access to the latest data.
Tone or style mismatches: If the response was correct but the tone or style didn’t meet the user’s expectations, adjust the Style settings in HALO. This allows you to customize the tone of voice, response length, and fallback options to better align with your brand identity.
By addressing these issues systematically, you can ensure your agent performs more reliably and delivers a better user experience.
Step 4: Test Your Changes
After making improvements, it’s crucial to test your agent again. Use the Test Center in HALO to simulate various scenarios. Test the same scenario that previously failed to ensure the issue has been resolved.
Tip: Don’t just test the specific question that failed. Also test variations of it to ensure your agent is flexible enough to handle different phrasings and edge cases.
Iterative Testing: If the issue persists, repeat the debugging steps until the desired outcome is achieved. Iterative testing is essential to ensure your agent performs consistently.
Bonus Tips for Debugging in HALO
Leverage Context: Use the Context feature to centrally manage variables like API keys or default values. This prevents errors caused by inconsistent settings.
Create Test Scenarios: Develop clear test scenarios that your agent should handle. This helps you systematically verify whether your agent is functioning correctly in different situations.
Start with Tools: Tools are deterministic and easier to debug than other components like knowledge or prompts. Always start by verifying the tool’s output.
Conclusion
Debugging in HALO doesn’t have to be a daunting process. By following a structured approach, starting with analyzing conversations and moving to improving and testing your agent, you can quickly and effectively resolve issues. With HALO’s powerful tools and features, you can continuously optimize your AI agent to ensure it delivers the best possible responses.
Happy Debugging!
