Code Execution
The Code Execution node is a powerful feature that allows you to write and execute custom Python code directly within your tool. This node is ideal for performing advanced computations, data transformations, or custom logic that cannot be achieved using other nodes. By leveraging Python, you can extend the functionality of your tools and handle complex scenarios with precision.
Overview
The Code Execution node enables you to write Python code in a dedicated editor and execute it during the tool's workflow. Input variables can be mapped to the function parameters, and the output of the code can be stored in a variable for use in subsequent steps.
Key Components
Code Editor
The code editor is where you write your Python code. The editor provides a clean and focused environment for coding, with syntax highlighting to improve readability. Please note that Python code blocks are separate environments in which HALO controls the allowed package imports and their permitted functionalities.
Notes on method access:
Module methods: Available by default for all allowed packages
Classes: Must be explicitly listed in the configuration to be used
Instance methods: Automatically available for allowed classes
Class methods: Must be explicitly enabled in the configuration for each class
Allowed Python Packages
Package | Classes | Class Methods |
|---|---|---|
| - | - |
| - | - |
| - | - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - | - |
| - | - |
| - | - |
| - | - |
|
| - |
|
| - |
| - | - |
| - | - |
| - | - |
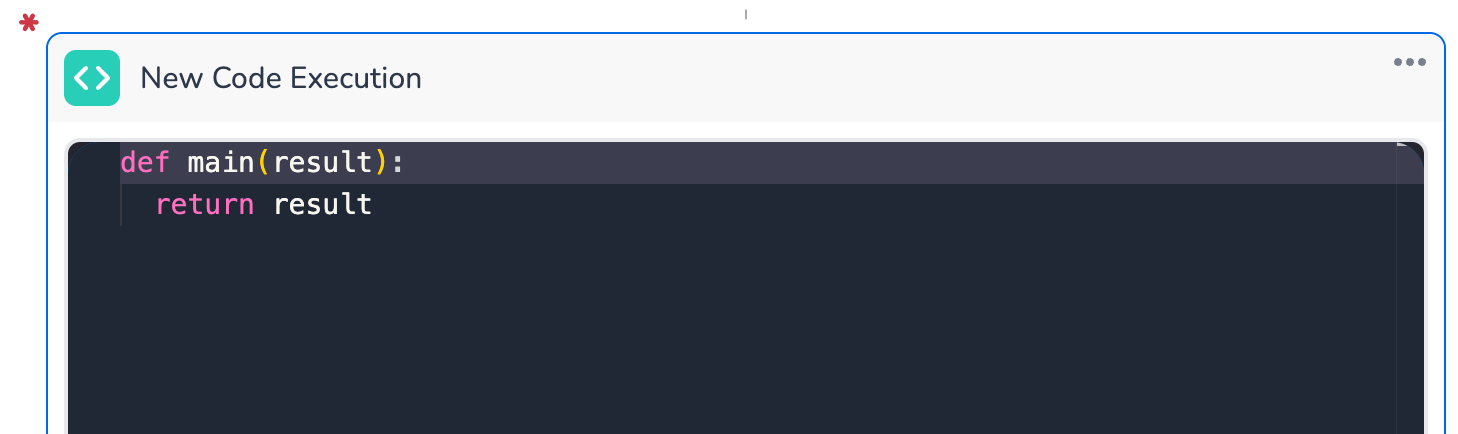
Function Definition: The code must be written inside the predefined main function. This function serves as the entry point for the code execution.
Example:
CODEdef main(result): # Your custom logic here return result
Return Statement: The
mainfunction must return a value. This value will be stored in the output variable and can be used in subsequent steps.
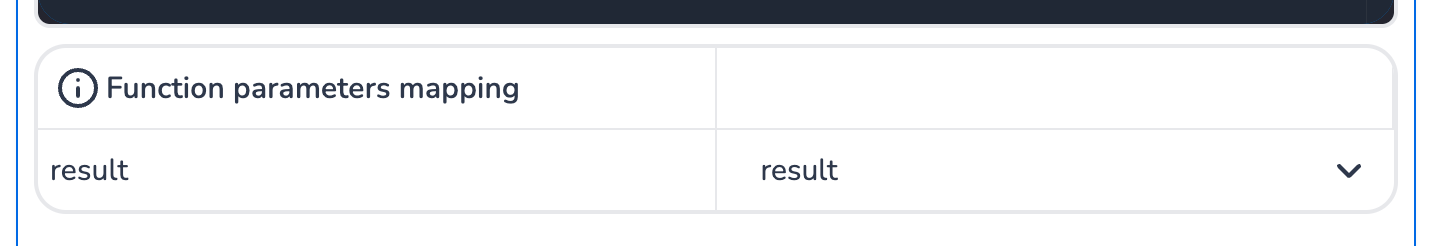
Function Parameters Mapping
The Function Parameters Mapping section allows you to map input variables to the parameters of the main function. This ensures that the data required for the code execution is passed correctly.
Input Variables: Select the input variables from the dropdown menu to map them to the function parameters.
Custom Parameters: You can define additional parameters in the
mainfunction and map them to specific variables or values.
Example:
If the
mainfunction is defined as:CODEdef main(a, b): return a + bYou would need to add
aandbin the parameters list and map them to a variable.
